Clicking the Build button beside a connection string setting brings up the Connection String Builder dialog, which allows you to visually build and test a connection string.
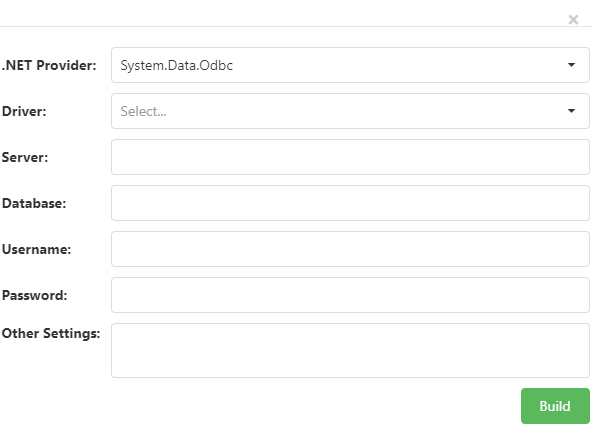
The first choice to make is the .NET provider to use: System.Data.Odbc for an ODBC data source, System.Data.OleDb for an OLE DB data source, MySql.Data.MySqlClient for a MySql data source, System.Data.SQLite for a SQLite data source, and System.Data.SqlClient for a Microsoft SQL Server data source. Which other settings appear depends on the .NET provider you selected.
-
Driver: select the driver to use from the drop-down list. This option is only visible for ODBC data sources.
-
Server: enter the name of the server to connect to. This option isn’t available for file-based databases such as Microsoft Access or SQLite.
-
Database: for file-based databases such as Microsoft Access or SQLite, enter the folder or path to the database file. For server-based databases such as Microsoft SQL Server or MySql, enter the database name.
-
User name: enter the user name to use or leave it blank for a trusted connection.
-
Password: enter the password to use or leave it blank for a trusted connection.
-
Other settings: enter any additional settings required by the driver or database.